Science Advances (the open-access version of Science Magazine) just published a paper I co-authored with Jane Kolodinsky from the University of Vermont. I suspect the paper's findings may raise a few eyebrows, as we find that opposition to GMOs in Vermont fell relative to that in the rest of the U.S. after mandatory labeling was adopted in that state.
Some background context might be useful here. Several years go, I was decidedly in the camp that thought imposition of mandatory labels would cause people to be more concerned about GMOs because it would signal that something was unsafe about the technology. Prominent scholars such as Cass Sunstein have argued the same. A few years ago, Marco Costanigro and I put this hypothesis to the test in a paper published by Food Policy, and we found little evidence (in a series of survey-based experiments) that the label per se neither increased or decreased aversion to GMOs. So, I was less convinced that this particular argument against mandatory GMO labeling was valid, but I was still unsure.
Then, last summer at the annual meetings of the Agricultural and Applied Economics Association (AAEA), I saw Jane present a paper based on survey data she collected in Vermont before and after mandatory labels went into place there. Her data suggested opposition to GMOs fell at faster rate after mandatory labels were in place. Despite my findings in Food Policy, I remained dubious and Jane and I went back and forth a bit on the robustness of her findings.
I'd been in enough conversations with Jane to know that we had different philosophical leanings about the desirability of GMOs, but this was an empirical question, so we put our differences aside and decided to join our data and put the hypothesis to the test. Through the Food Demand Survey (FooDS), I had been collecting nationwide data on consumer's concerns about GMOs, and I suggested we combine our two sets of data and do a true "difference-in-difference" test: Did the difference in concern among consumers in VT and the result of the US increase or decrease after mandatory labeling was adopted in VT?
Our article in Science Advances has the result:
“This research aims to help resolve this issue using a data set containing more than 7800 observations that measures levels of opposition in a national control group compared to levels in Vermont, the only U.S. state to have implemented mandatory labeling of GE foods. Difference-in-difference estimates of opposition to GE food before and after mandatory labeling show that the labeling policy led to a 19% reduction in opposition to GE food. The findings help provide insights into the psychology of consumers’ risk perceptions that can be used in communicating the benefits and risks of genetic engineering technology to the public.”
One important caveat should be mentioned here. Our result does NOT suggest people will suddenly support GMOs once mandatory labels are in place. Rather, our findings suggest that people will be somewhat less opposed than they were prior to labels. I mention this because in the wake of my paper with Marco in Food Policy some of the media's interpretation of our results (such as that of the New York Times editorial board), could have been construed as suggesting that imposition of mandatory labels would not cause economic harm. That may or may not be true. But, this new study suggest that labels per se may in fact reduce opposition.
It was great to work with Jane on this project, and for me it was a good lesson to test your beliefs, particularly when there are theoretical reasons that could support the opposing point of view.
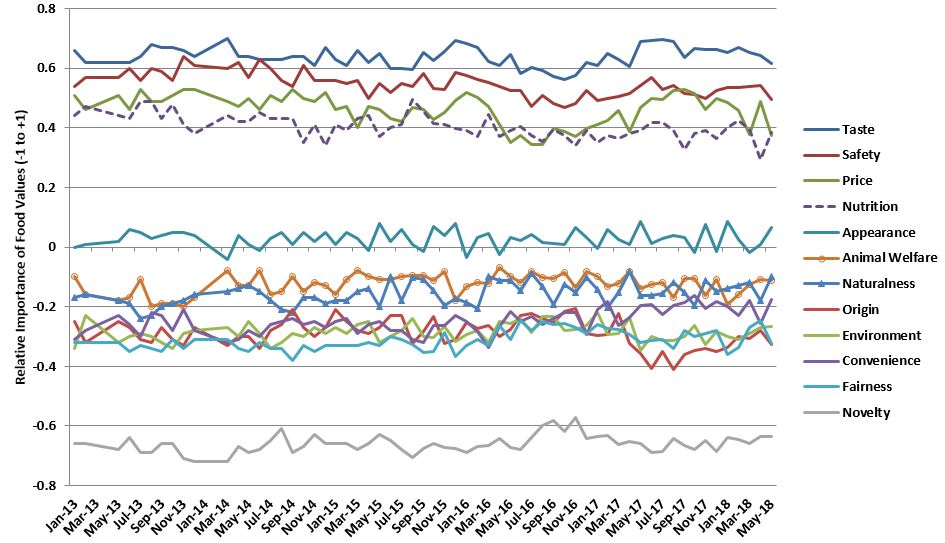
I'll end with a key graph from the paper.